What is Organic Food and Why Should You Care?: Have you ever wondered what lies behind the label of organic food? Beyond the buzzwords and claims, what makes organic food distinct, and why should you care? In this exploration, we unravel the world of organic food, its health and environmental benefits, the growing demand for it, and how you can seamlessly integrate it into your life. Join us on a journey to understand the essence of organic food and why it’s a choice that resonates with health-conscious individuals and eco-conscious consumers alike.
What is Organic Food?


Organic food is far more than just a label; it’s a commitment to producing food without artificial chemicals, hormones, antibiotics, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Organic farming practices are rooted in the belief that food should be grown and raised in a manner that enhances soil quality, conserves water, reduces pollution, and prioritizes animal welfare. It’s a way of farming that respects nature and promotes health.
The Benefits for Health and Environment:


Organic food isn’t just a trend; it’s a lifestyle choice that offers numerous benefits. Studies indicate that organic food often contains higher levels of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals than conventional food. These antioxidants help safeguard your cells and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Additionally, organic food typically contains fewer pesticides and harmful bacteria, reducing the potential harm to your nervous and reproductive systems.
The Growth of Organic Food Market and Consumer Demand:
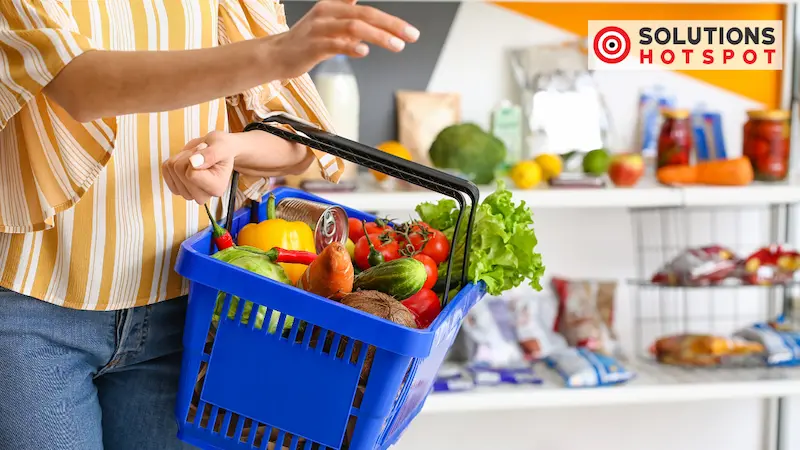


Over the last two decades, the demand for organic food has experienced remarkable growth. In 2020, U.S. consumers spent $56 billion on organic produce, signifying a 13% increase from 2019. Globally, the organic food and beverages market reached an estimated $211.44 billion in 2020 and is projected to grow at a 16.44% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2020 to 2025. Commonly purchased organic foods include fruits, vegetables, grains, dairy products, and meat.
By choosing organic food, you support a more sustainable and ethical approach to food production. You also savor fresher, more flavorful, and nutritionally superior food that can contribute to your health and well-being.
What Makes Food Organic?
Organic food isn’t just about what’s inside the packaging; it’s about how it’s grown and processed. To earn organic certification, a food product must consist of at least 95 percent certified organic content. This means that ingredients are cultivated without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, GMOs, antibiotics, hormones, or irradiation. The remaining 5 percent of non-organic ingredients must be approved by the USDA National Organic Program (NOP), which meticulously oversees and enforces organic standards.
Organic Farming vs. Conventional Farming:
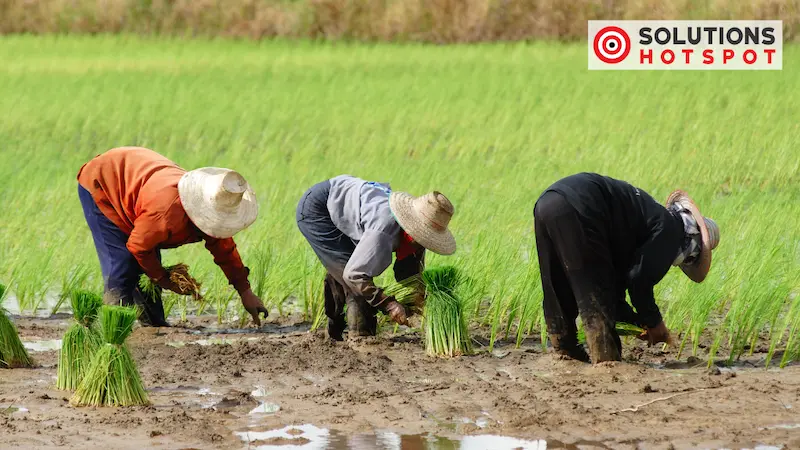


Organic farming practices extend beyond the plate. They aim to preserve soil, water, biodiversity, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and minimize pollution. Organic farmers employ natural methods like crop rotation, composting, mulching, and biological pest control to maintain soil fertility and deter pests and diseases. Additionally, they provide humane living conditions for their animals, including access to pasture, fresh air, sunlight, and clean water.
Common Organic Foods and Products:
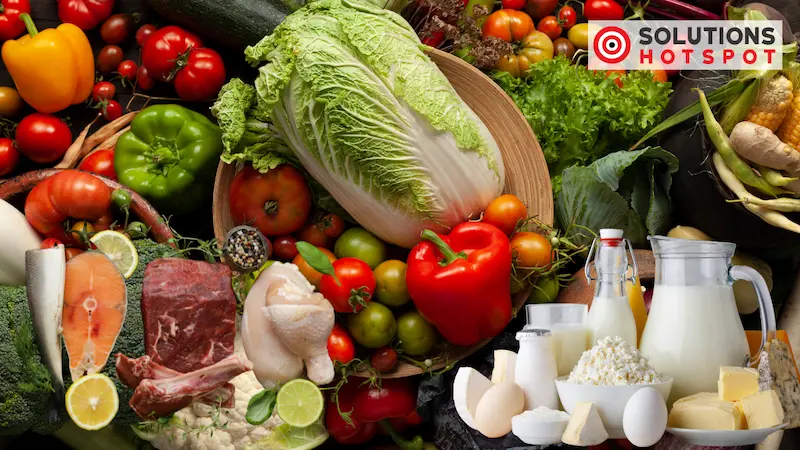


The world of organic extends well beyond fruits and vegetables. Common organic offerings include grains, dairy, eggs, meat, poultry, honey, coffee, tea, wine, beer, cosmetics, textiles, and household cleaners. Organic foods often bear the USDA organic seal or the words “certified organic” on the packaging. It’s worth noting that certain products may contain less than 95 percent organic content but still identify specific organic ingredients in the ingredients list.
Why Choose Organic Food?
The choice to embrace organic food is rooted in its numerous advantages. Research reveals that organic food boasts higher levels of antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, and beneficial fatty acids compared to conventional counterparts. Organic food also contains fewer pesticide residues, heavy metals, and antibiotic-resistant bacteria, ensuring you’re consuming a cleaner, healthier option.
How to Choose and Use Organic Food:
Incorporating organic food into your life is both fulfilling and impactful. Here are some practical tips for finding, buying, storing, and enjoying organic food:
- Look for the USDA organic seal or a reputable certifying agency’s label on packaging.
- Compare prices and quality of different organic brands and sources.
- Seek sales, discounts, coupons, or bulk deals to save money on organic purchases.
- Consider joining a community-supported agriculture (CSA) program or a buying club for convenient access to organic produce.
- Follow standard food storage guidelines for perishable and dry organic goods.
- Gradually increase your organic food intake by replacing regular items with organic alternatives.

Conclusion:
Organic food isn’t merely about what you eat; it’s about making a conscious choice that impacts your health, the environment, and the future of farming. This lifestyle offers a path to a vibrant, more resilient you while supporting farmers who prioritize product quality and customer well-being. By embracing organic food, you join a growing community dedicated to sustainable agriculture and the planet’s protection.
The journey to understanding organic food has brought us to a world of flavorful, nutrient-rich, and conscientious eating. Why not embark on your own organic food experience and share your discoveries with us? Your experience and feedback are valuable, and we’d love to hear from you. Join the organic food movement and savor the benefits of a healthier, more sustainable, and tastier lifestyle. Thank you for exploring the world of organic food with us.
What is Organic Food and Why Should You Care?
FAQ
Q1. What is organic food?
A. Organic food is produced using farming methods that do not involve synthetic pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Organic farming practices are designed to promote soil and water conservation, protect biodiversity, and support animal welfare.
Q2. Why should I care about organic food?
A. There are many reasons to choose organic food. Organic food is often more nutritious than conventionally grown food, as it contains higher levels of antioxidants and other beneficial nutrients. Organic food is also free of synthetic pesticides and herbicides, which can have harmful effects on human health and the environment. Additionally, organic farming practices are better for the environment, as they help to conserve soil and water resources and protect biodiversity.
Q3. Is organic food more expensive than conventionally grown food?
A. Organic food can be more expensive than conventionally grown food, but the price difference is often not as large as people think. Additionally, there are many ways to save money on organic food, such as buying in bulk, shopping at farmers’ markets, and growing your own food.
Q4. Is organic food worth the extra cost?
A. It is a personal decision. Some people believe that the health and environmental benefits of organic food are worth the higher price, while others are not as concerned about these issues. Ultimately, the decision of whether or not to buy organic food is up to you.
Q5. How can I find organic food?
A. Organic food is becoming increasingly available in grocery stores, farmers’ markets, and online retailers. You can also find organic food at some restaurants and cafes. If you are not sure where to find organic food in your area, you can search for local organic farms and CSAs (community-supported agriculture) programs.

